- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Note
This report aims to try out one of the mindmapping software where this report is my undergraduate assignment in the 2013 on Technology Application for Education course and I translated the original Indonesian to English myself. This assignment has never been published anywhere and I, as the author and copyright holder, license this assignment customized CC-BY-SA where anyone can share, copy, republish, and sell on the condition that to include my name as the author and notify that the original and open version available here.
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background
Mind maps are usually drawn manually, usually on paper, on a chalkboard or elsewhere. How to make a mind map on a computer? Recently a type of software, namely mindmapping software was written. The mind mapping software that will be discussed is Semantik. Semantik is a mindmapping software on Linux KDE. Why choose Semantik? Because Semantik is a new software currently on Linux KDE.
1.2 Objective
Try minemapping software
1.3 Question
- What features are available in Semantik?
- How mindmaps can Semantik generate?
Chapter 2 Literature Review
Mindmap consists of 2 words, namely "mind" and "map". Mind is everything that is on our mind. Map is a map that has a path to reach a place. A mindmap is a mapping of thoughts.
The mindmap consists of a parent. Then the branch against the parent is called a child. This child is something related to the parent. It could be something that forms the parent, something that affects the parent, something related to the parent or other similar things. Usually in mindmap a parent is created by branching the many children that makes up the parent. Then the child can be branched again by the child from the child that makes up the child parent. The art of mindmapping is branching out as many as possible.
Mindmaps that are usually drawn manually on paper are now available on computer software for mindmapping. Examples of software:
Chapter 3 Discussion
3.1 Semantik Installation on Linux KDE
Instal Semantik online using apt (advanced packaging tool) by typing “apt-get install semantik”.
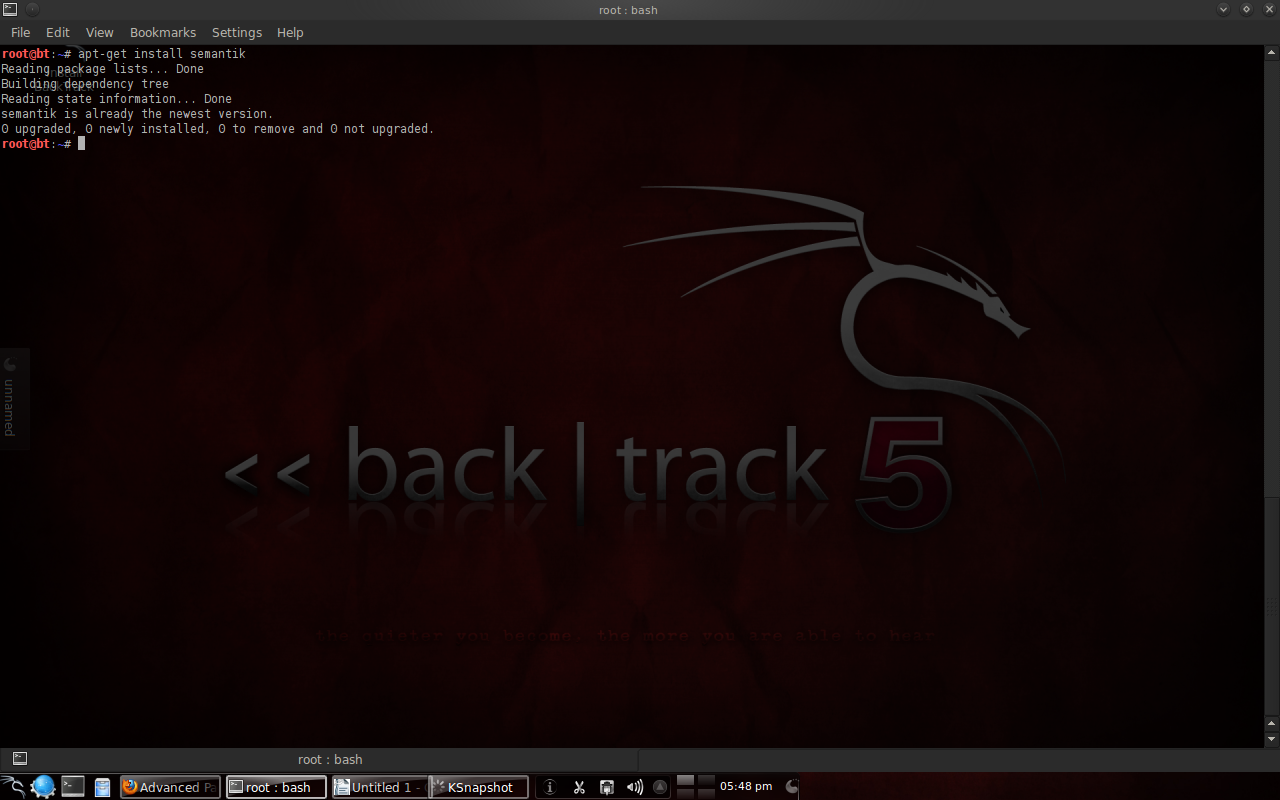
To open Semantik, just type “semantik”.
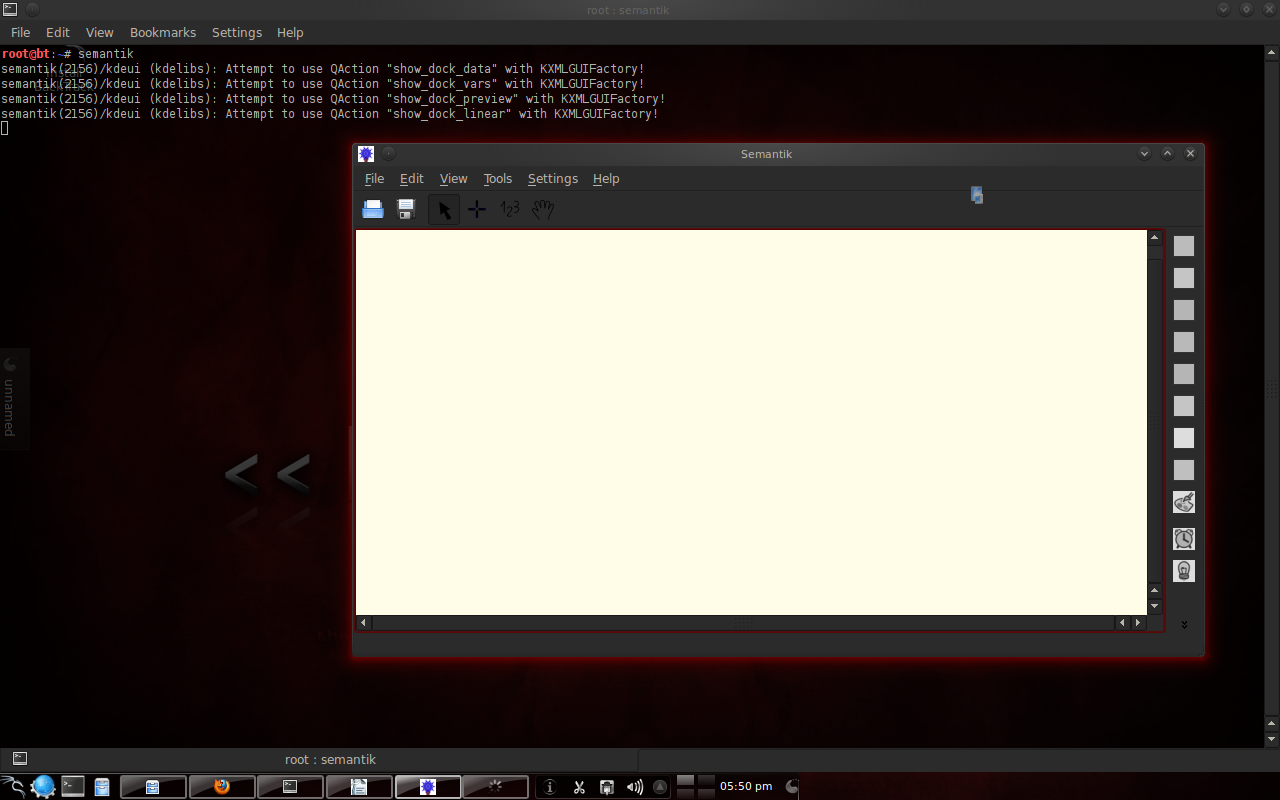
3.2 Features in Semantik
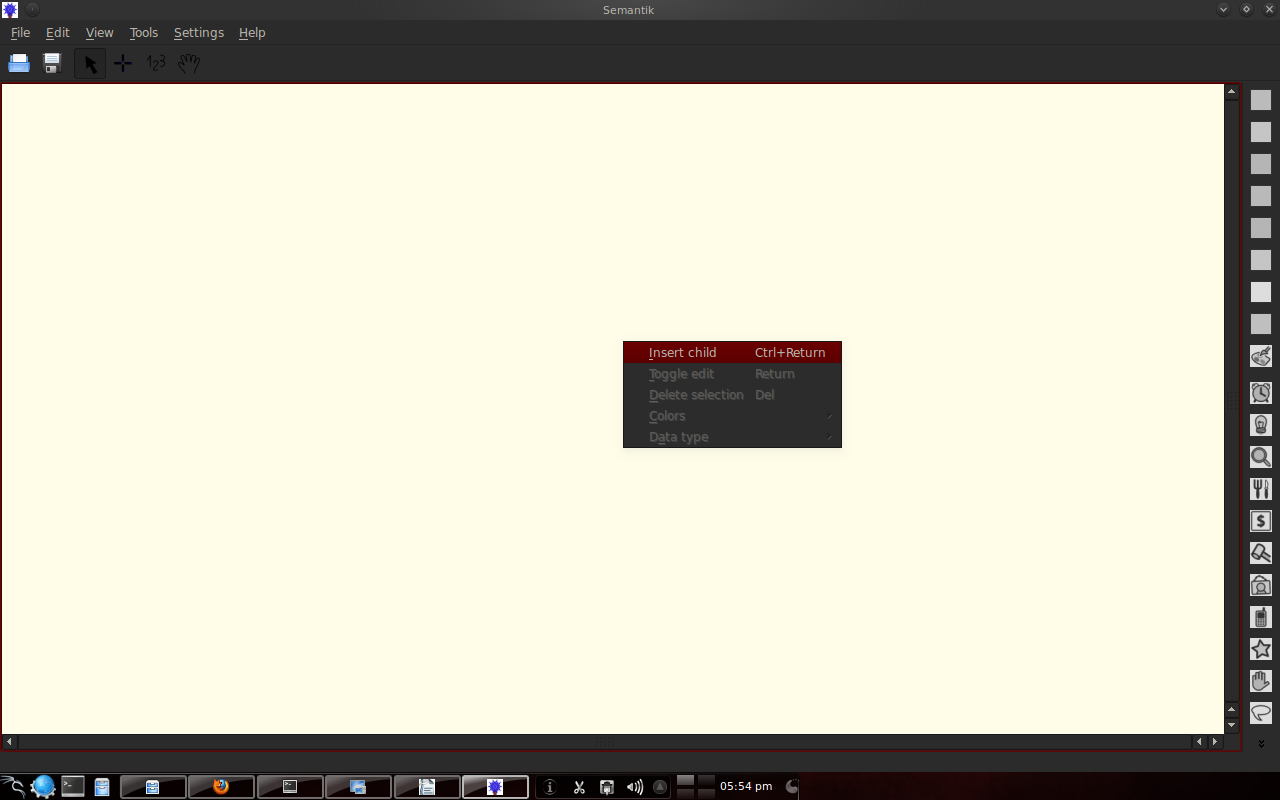
To start, right click and select insert child.
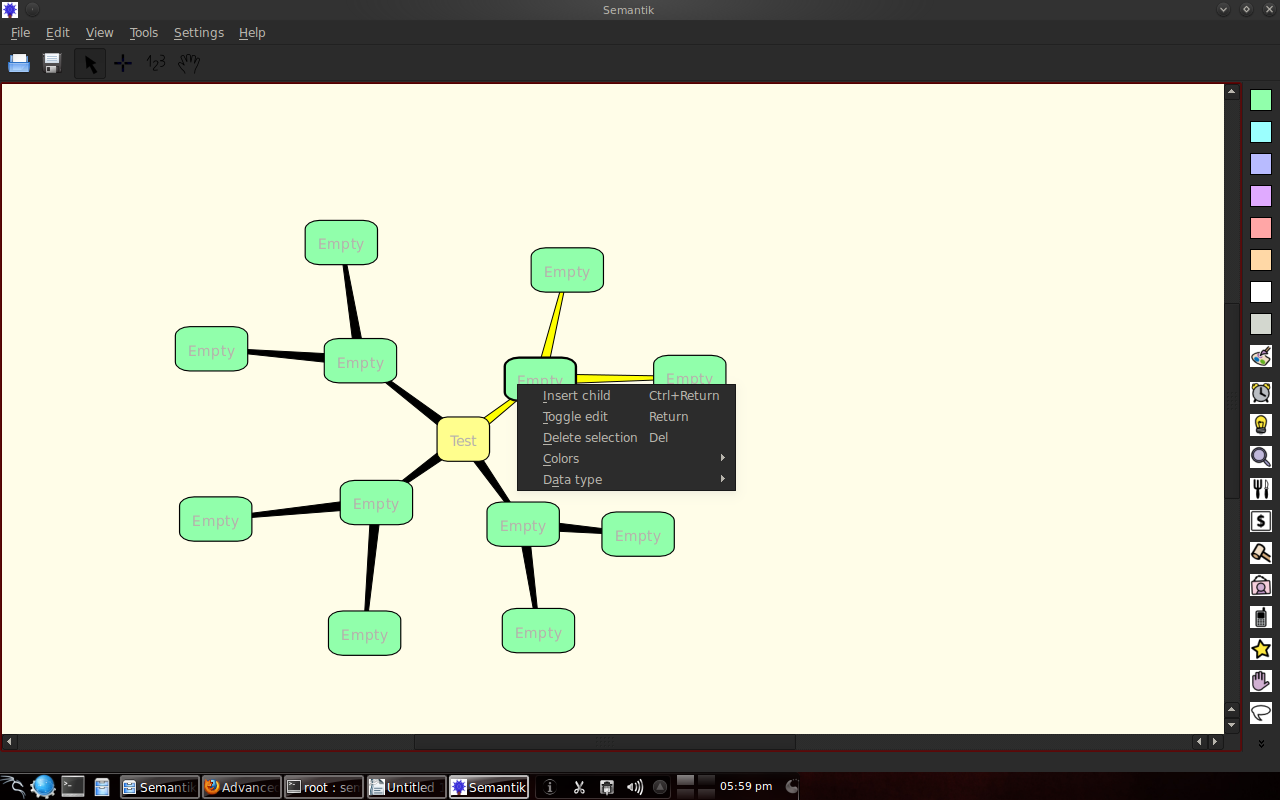
By doing the same thing by placing the cursor on the parent or child, you can create branches.
Select all options in the "view" to see another "preview".
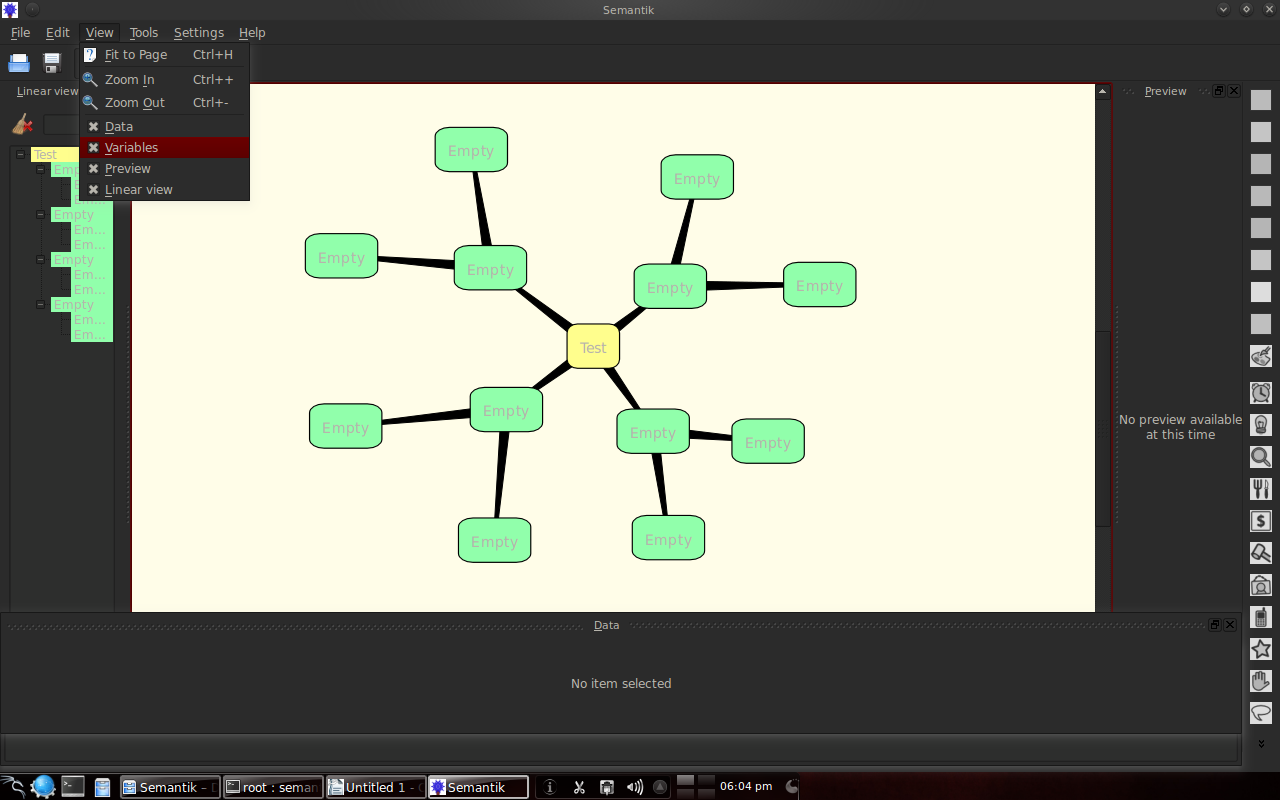
Dengan klik kanan pada suatu kotak, maka dapat membikin cabang baru, edit tulisan, memilih warna dan memilih tipe data untuk dimasukkan ke dalamnya.
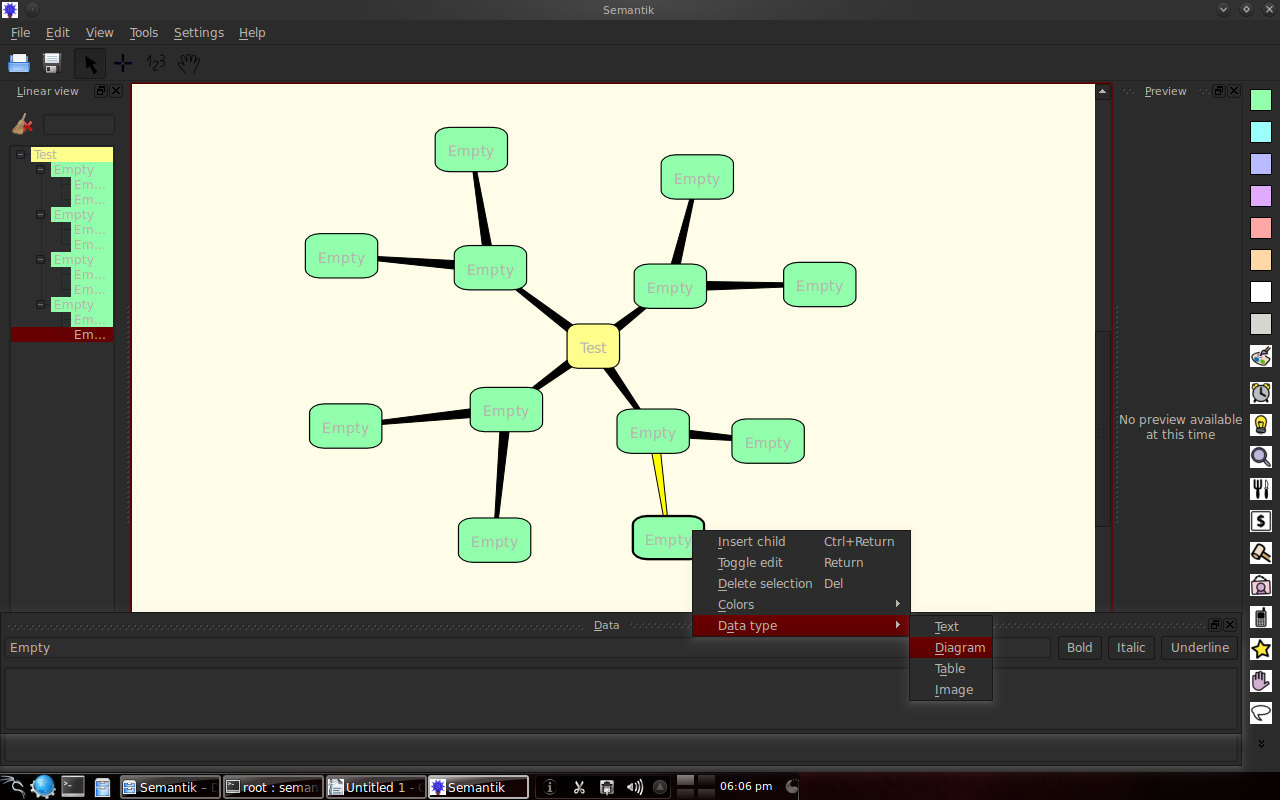
Examples of data types can be seen below:
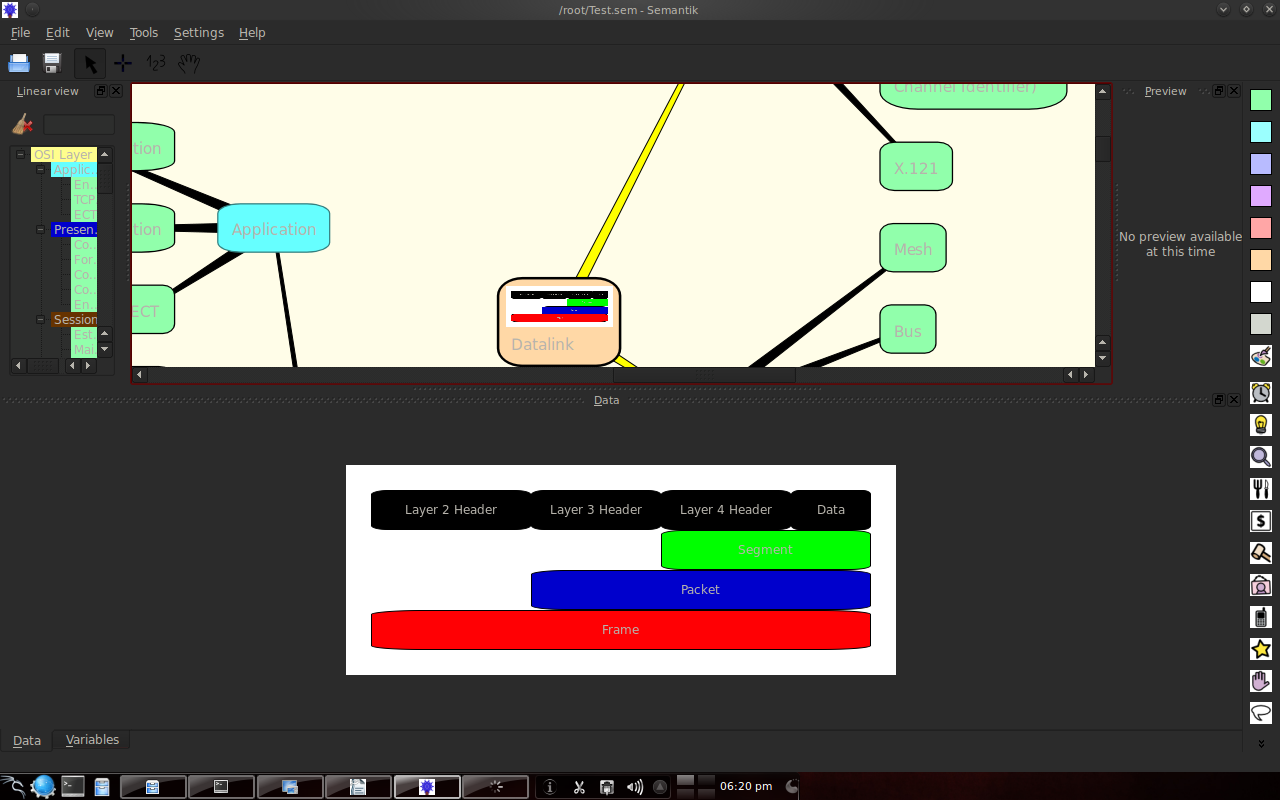
There is a generate feature to display presentation forms, web formats or others.
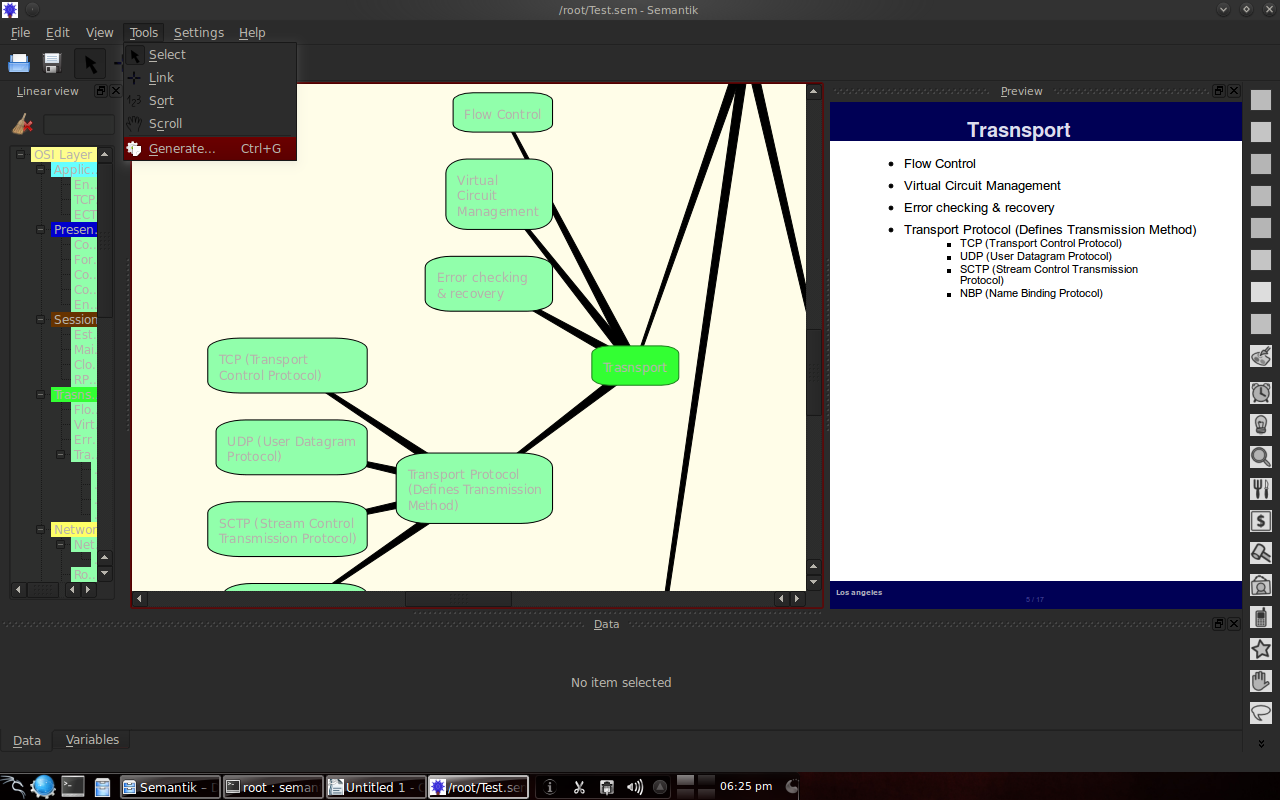
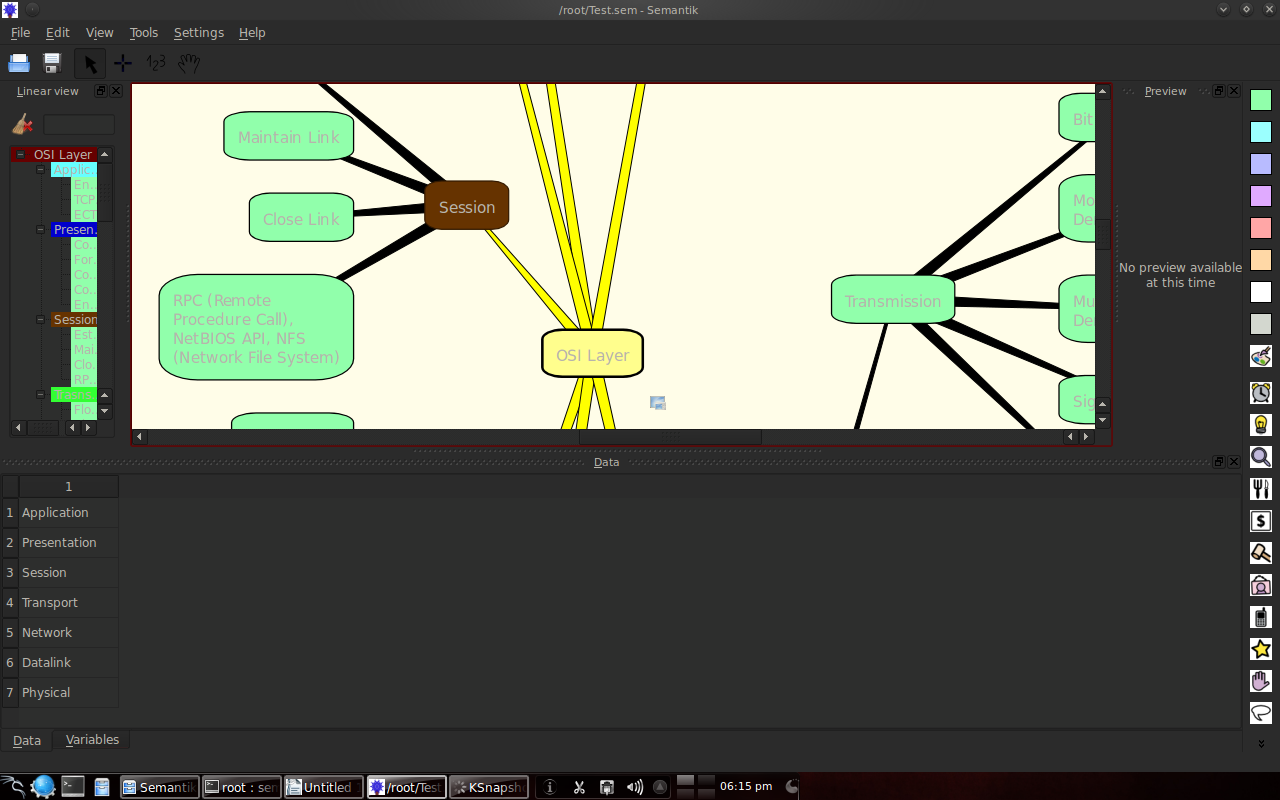
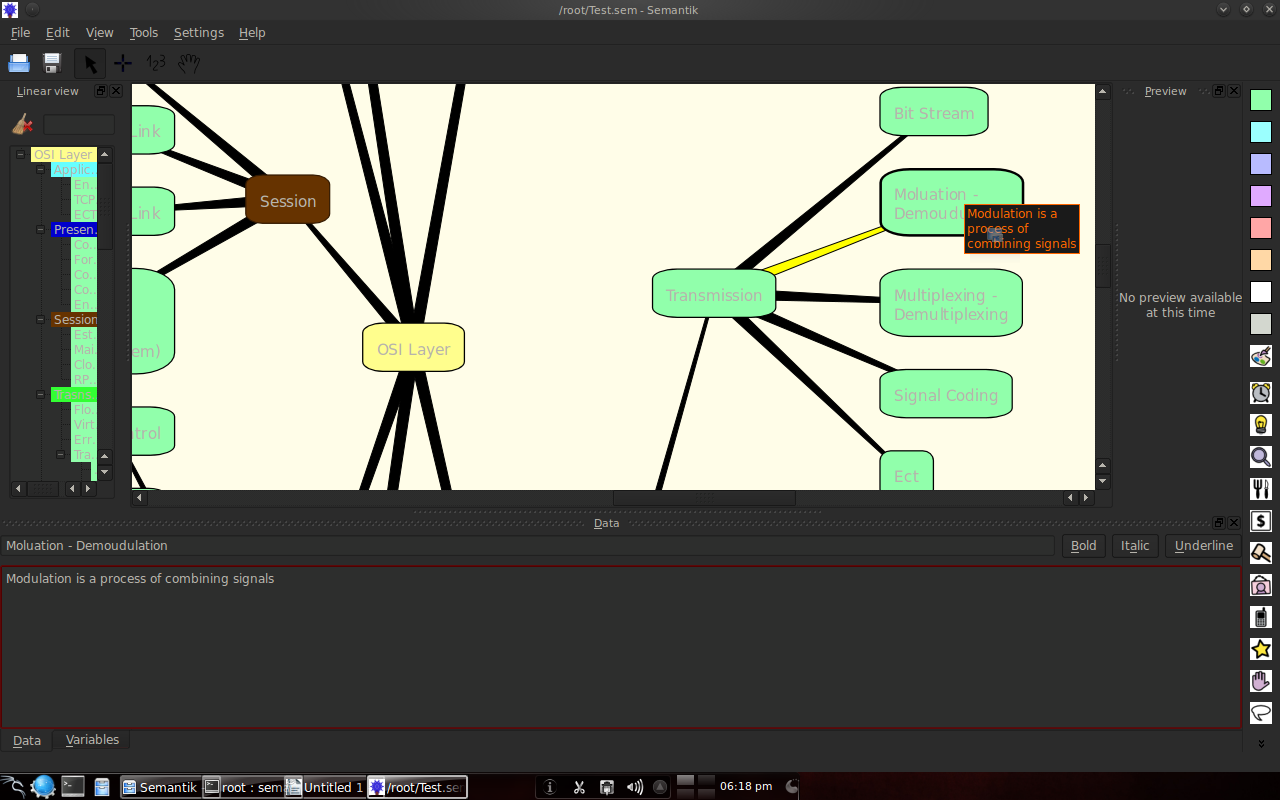
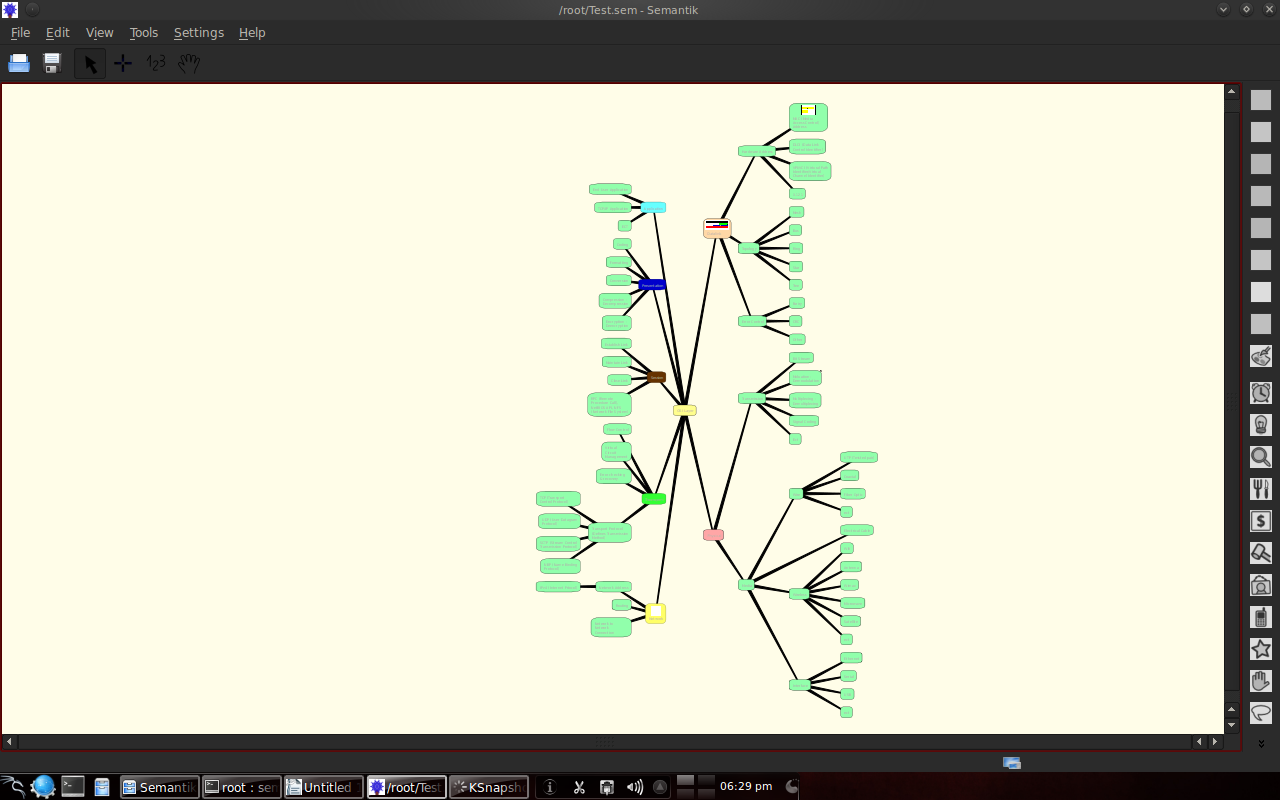
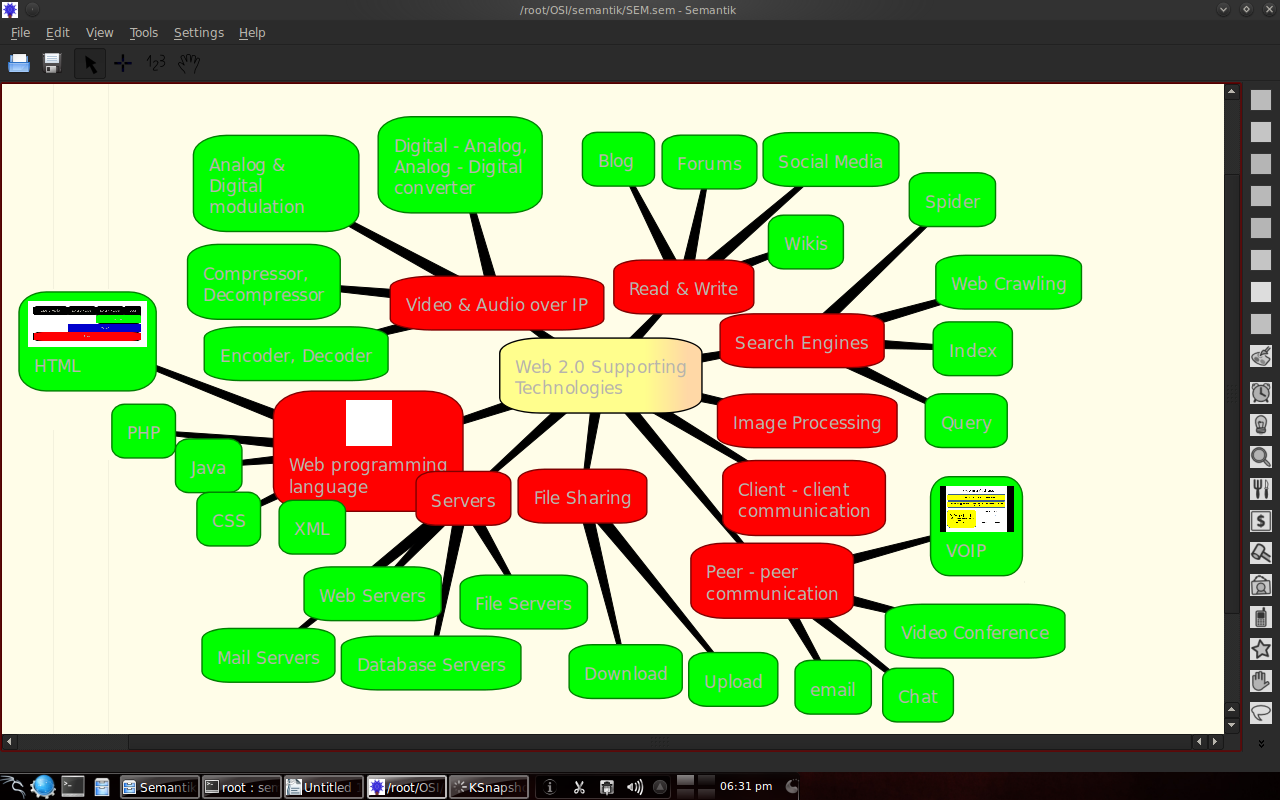
3.3 Example of the results of making a mindmap with Semantik
The following is an example of making an OSI layer and Web 2.0 mindmap.
Chapter 4 Closing
4.1 Conclusion
The conclusion that can be reached in this report is that Semantik software is sufficient for making a mindmap. Semantik is also open source software and is still developing. In the future, we hope that Semantik will add other features, such as flash animation.
Mirror
- https://www.publish0x.com/fajar-purnama-academics/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux-xnlvwzd?a=4oeEw0Yb0B&tid=blogger
- https://0fajarpurnama0.github.io/bachelor/2020/11/23/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux
- https://0fajarpurnama0.medium.com/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux-3208dacf7c6b
- https://hicc.cs.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/~fajar/bachelor/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux
- https://blurt.buzz/blurtech/@fajar.purnama/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux?referral=fajar.purnama
- https://0darkking0.blogspot.com/2020/11/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux.html
- https://hive.blog/technology/@fajar.purnama/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux?referral=fajar.purnama
- https://0fajarpurnama0.cloudaccess.host/index.php/9-fajar-purnama-academics/113-mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux
- https://steemit.com/computers/@fajar.purnama/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux?r=fajar.purnama
- http://0fajarpurnama0.weebly.com/blog/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux
- https://0fajarpurnama0.wixsite.com/0fajarpurnama0/post/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux
- https://read.cash/@FajarPurnama/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux-73658aef
- https://www.uptrennd.com/post-detail/mindmapping-using-semantik-on-kde-linux~ODE2MjUz
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment